Advanced Electronic Signature (AES)
9 min read
An Advanced Electronic Signature (AES or AdES) is one of the three types of eSignatures introduced by the EU regulation eIDAS. Since it’s unique, trackable, and linked to the signer by an electronic certificate, AES is one of the most secure ways to sign a contract. In this guide, you’ll learn everything about AES, from what it is exactly, how you can obtain it, to when you should use it.
Table of contents
- What is Advanced Electronic Signature (AES)?
- What’s Included in an Advanced Electronic Signature?
- How to Sign a Document Using Advanced Electronic Signature?
- When to Use an Advanced eSignature?
- Security & Legality
- Advanced Electronic Signatures vs. Qualified Electronic Signatures
- What Are the Benefits of Using Advanced Electronic Signatures?
- Summary
- Frequently Asked Questions
What is Advanced Electronic Signature (AES)?
An advanced electronic signature (AES or AdES) is a type of eSignature that offers a high level of security and reliability by using one or more types of ID verification, like facial identification or an OTP (one-time password), to verify the signer’s identity.
Advanced electronic signatures are unique, identifiable, and detectable.
When you sign a document using the advanced method, a unique digital certificate will be generated and attached to your signature. This certificate works like a link between you and your signature and it’s coded with strong cryptographic algorithms. Since there’s only one link per signature/person, it cannot be forged or tampered with easily.
You have probably used AES already. An example of AES would be signing an NDA through email and entering a PIN code you received via SMS to prove your identity.
This type of signature was introduced by EU under the Digital Identity Regulation 910/2014 (better known as eIDAS) and it’s widely recognizable and effective throughout the EU and the world.
💡 Good to know: The use of the word “Advanced” for electronic signature is only used in the eIDAS documentation; other legal regulations such as UETA/ESIGN in the USA or ZertES in Switzerland also outline special requirements for the legality of electronic signatures that are similar to eIDAS definitions.
What Are the Requirements for Advanced Electronic Signatures?
For an Electronic Signature to be considered advanced under eIDAS, it should meet the following criteria:
- Directly linked to the signer
- Able to identify the signer
- Tied to the signed data in a way that any changes can be detected
- Created using data that only the signer can access and control with high confidence


Based on these criteria, AES is unique, identifiable, and detectable.
Because of the high level of assurance it provides, using AES is especially useful when you want to sign legal agreements where verifying the other party’s identity is crucial to you and you need to ensure the contract cannot be repudiated.
What’s Included in an Advanced Electronic Signature?
An Advanced Electronic Signature has several layers of elements, including:


The eSignature Graphic
This is the visual representation of the signature, like a typed name, drawing, or scanned image of a wet signature.
ID Verification
This confirms the signer’s identity through methods like government ID checks or multi-factor authentication (MFA).
Here are some of the methods for identity proof used in Advanced Electronic Siging:
- Valid ID: issued by the government like a driver’s license
- Biometric Detection: such as facial identification and fingerprint
- 2FA or MFA: Entering a PIN received by email or text message
Depending on the case, you may only need one verification method.
Cryptographic Keys
These are digital keys used to verify the signature, which guarantees that only the signer can create the signature.
Public key
It’s connected with the signer’s identity (like name and organization) and the graphic representation of the signature itself.
Anyone can access this public key to verify the signer’s identity when they see the signature.
Private key
It’s a unique mathematical code that is used to create the signature and works like a digital fingerprint of the document.
The public key verifies the signer’s identity, while the private key creates the unique signature for the document. They work together to ensure the authenticity and integrity of the e-signature.
Serial Number
This unique number identifies the specific e-signature. This number can be used for tracking and validating the signature.
Validity Period
This part shows the timeframe for which the signature is valid.
CA Information
A Certification Authority (CA) is a trusted third-party company that stores, signs, and issues digital certificates. CAs are the agents between the signer and legal institutions that vouch for the validity of the public key and the signer’s identity linked to it.
How to Sign a Document Using Advanced Electronic Signature?
To electronically sign a document using an Advanced Electronic Signature (AES), you should use an eSignature platform that complies with eIDAS eSigning regulation.
To quickly and securely sign your documents and send signature requests, you can use fynk.
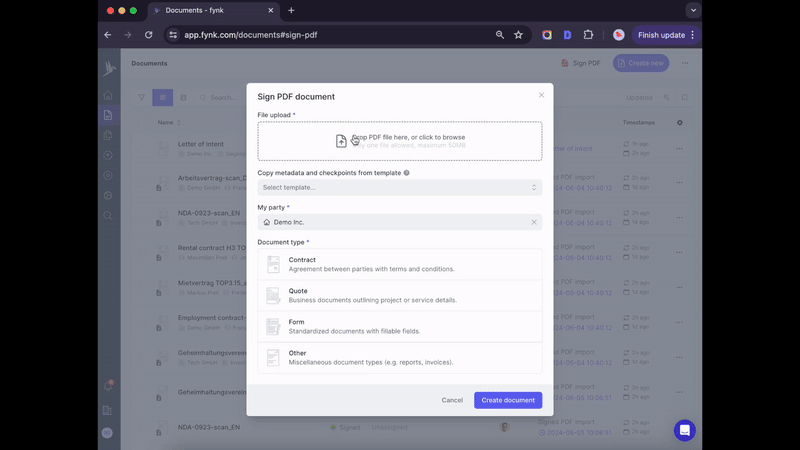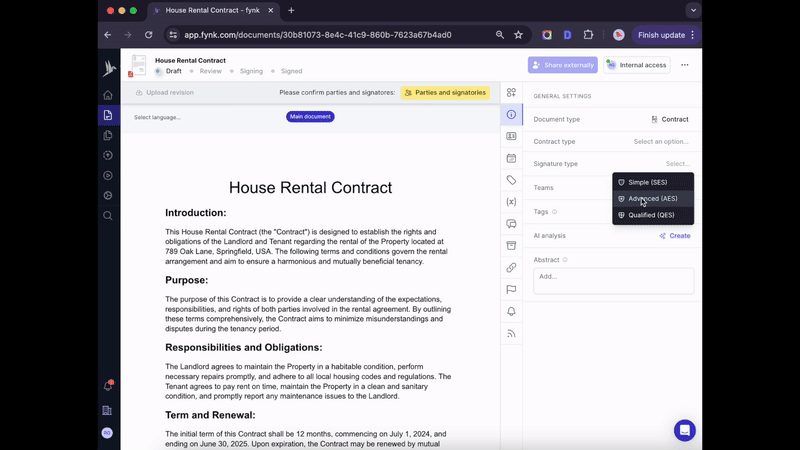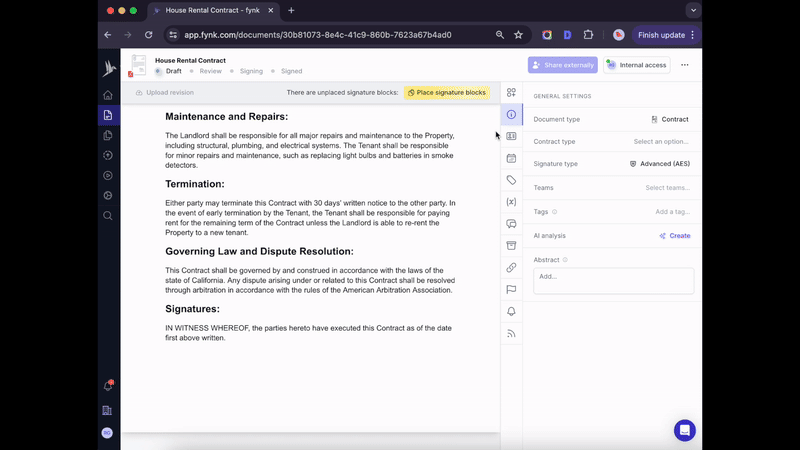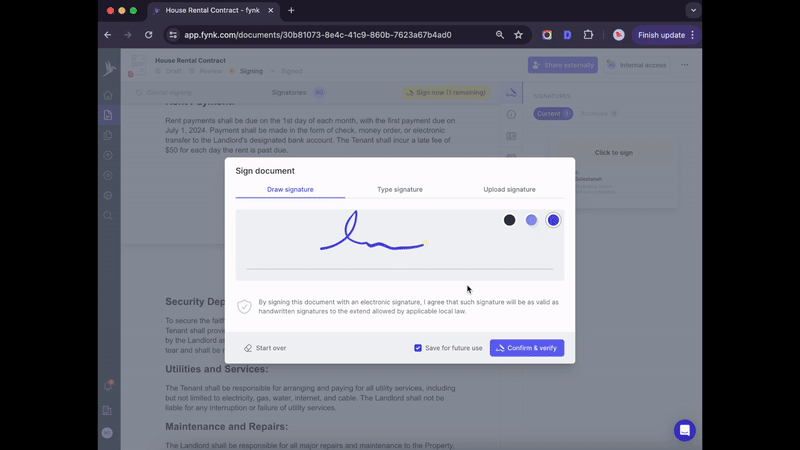
Process
Here’s the process of using an Advanced Electronic Signature on fynk:
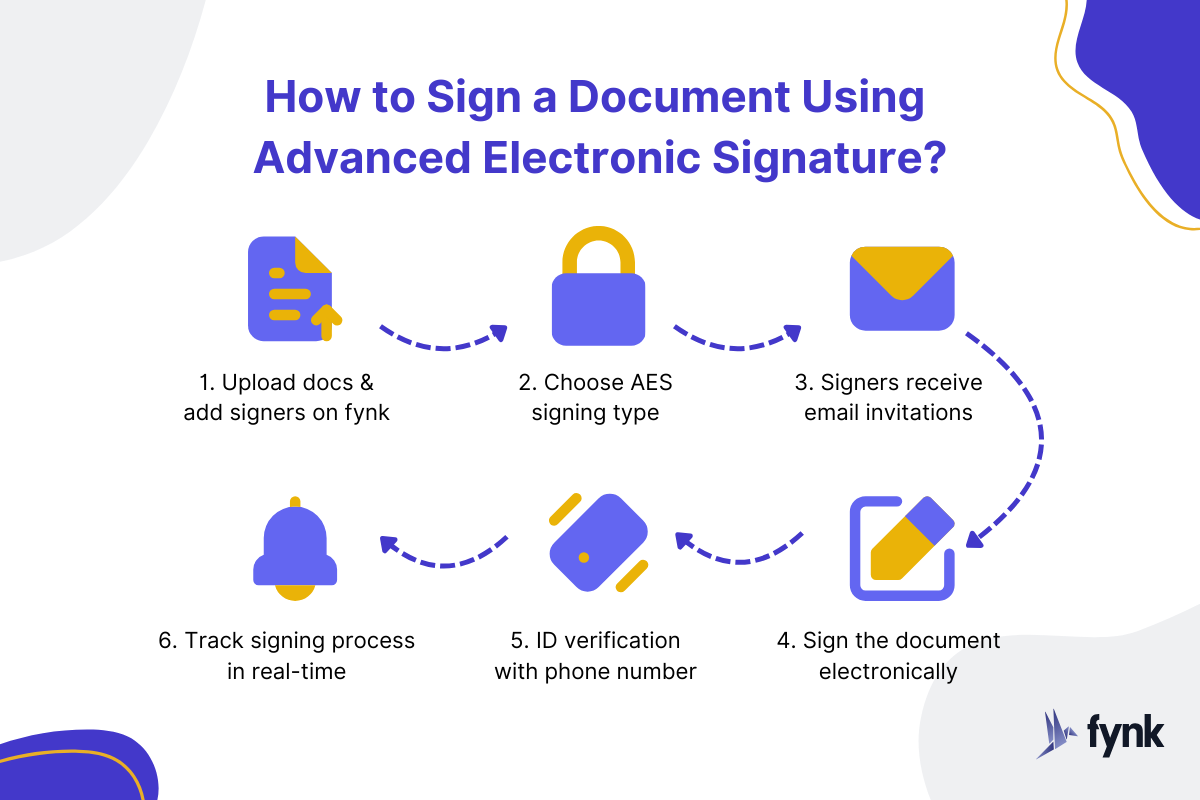

- Upload documents and add all signatories
- Choose AES as the signature type
- Signers get an email to sign on fynk (no login required)
- Sign using a touchpad, upload, or take a photo of the wet signature
- Verify ID with code sent to the phone
- Receive notifications on each signature
Why Should You Use fynk?
fynk’s digital contract management software is safe, fast, and secure. You can legally sign documents using simple, advanced, or qualified signatures from any device with our eIDAS-compliant platform.
Your signature data is in safe hands. Designed to be GDPR-compliant, it’s hosted on ISO/IEC 27001 certified servers.

Here are some of the advantages of using fynk:
- Workflows: Use templates, bulk actions, and legal document automation for efficiency.
- All-in-one platform: Create, sign, and manage contracts in one place.
- Highly secure: Ensures compliance and legally binding signatures.
- Collaboration features: Work together seamlessly on contracts.
- Time-saving: Frees up your time for more important tasks.
- User-friendly: Easy to use for everyone, anywhere.
When to Use an Advanced eSignature?
Use Advanced Electronic Signatures (AES) when signing contracts with high to medium levels of risk, when you need to comply with regulations, and in case of a strong need for non-repudiation.
1. For Medium to High-Risk Transactions
When it comes to a very large amount of money, always consider using an Advanced Electronic Signature. The situation may include:
- High-Value contracts
- Real Estate transactions
- Banking and financial transactions
2. For Compliance with Regulations
- Submitting tax returns electronically to a government agency
- Filing annual company report with a regulatory body
- Issuing a digital prescription to a patient
3. Strong Need for Non-Repudiation
Non-repudiation is an agreement in which you can’t deny your involvement in an action. You can use AES to sign this type of contract.
- Signing a non-disclosure agreement (NDA) with a business partner
- Issuing a digital certificate for a customer to access a secure system
- A court order being served electronically on a defendant in a legal case
Security & Legality
How Secure Are the Advanced Electronic Signatures?
In terms of the level of security provided, Advanced Electronic Signatures (AES) offer a high level of protection. However, they are not the most secure eSignature you can get.
They are significantly more secure than Simple Electronic Signatures (SES), which don’t have any identification requirements. However, Qualified Electronic Signatures (QES) offer the highest level of security compared to AES.
Therefore, you can use AES for documents with moderate to high levels of risk, such as NDAs or house contracts. If you need to sign highly sensitive documents, however, it’s best to consider using a Qualified Electronic Signature (QES).
Are Advanced Electronic Signatures Legally Binding?
Yes, according to Article 25 of eIDAS, which ensures the legality of all electronic signatures (including AES) with are legally binding.
The original text says:
An electronic signature shall not be denied legal effect and admissibility as evidence in legal proceedings solely on the grounds that it is in an electronic form or that it does not meet the requirements for qualified electronic signatures.
When you use AES, you need to ensure that the certificate supporting your signature comes from a trusted provider, was valid at the time of signing, and the signed data hasn’t been tampered with.
❗Remember: all levels of electronic signatures—Simple, Advanced, and Qualified—carry the same validity and legal value.
If something goes wrong during the eSignature process, the responsibility typically falls on the trust service provider.
If the provider isn’t qualified, you would need to prove their fault. However, if they are qualified, it’s presumed they’re at fault unless they can prove otherwise.
It’s important to know that the rules about liability are based on the laws of your country, so the legal framework there will determine who’s responsible.
Advanced Electronic Signatures vs. Qualified Electronic Signatures
Both Advanced Electronic Signatures (AES) and Qualified Electronic Signatures (QES) are legally binding electronic signatures. However, they differ in terms of security features and use cases.
Here’s a breakdown of the key differences based on various criteria:
| Type of eSignature | Advanced Electronic Signature (AES) | Qualified Electronic Signature (QES) |
|---|---|---|
| Security Level | High 🔒 | Very High 🔐 |
| Identification | Strong, using one or more ID verification 🛡️ | Very Strong, verified through a qualified certificate 🌟 |
| Creation Device | Any device 📱💻 | Must use a qualified electronic signature creation device or software 🖥️ |
| Legal Assurance | High, but varies by context 📜 | Equivalent to a handwritten signature, recognized across the EU 🇪🇺 |
| Use Cases | Business contracts, moderate security transactions 🤝 | High-value transactions, legal filings, governmental use 🏛️ |
The biggest advantage of QES over AES is the higher level of security that it provides. Advanced Electronic Signatures (AES) are highly secure, however, Qualified Electronic Signatures (QES) are even safer. In fact, QES are equivalent to the hand-written signatures.
Another difference between these two is that when using Advanced eSignatures, you’re free to sign using any device in your proposal, but for Qualified signatures, you can only sign using a qualified device.
For example, you may ask to install trusted software, or even cryptographic hardware to be able to carry out the signing process.
On the other hand, normally a PIN code or other type of 2FA is enough to validate an Advanced Electronic Signature.
What Are the Benefits of Using Advanced Electronic Signatures?
Fast Signing
The process of signing a contract using AES is quite simple and it only takes you a few minutes to complete. There’s no need to print, scan, or email anything.
Secure Process
All third-party platforms that provide Advanced Electronic Signatures are bound to comply with eIDAS regulations. That means they use cryptographic techniques to verify the signer’s identification to prevent any signature from being tampered with, forgery, or unauthorized access.
Globally Recognizable
Advanced Electronic Signatures are widely recognized around the globe due to their high level of security and integrity. Their unique identification features and strict compliance with regulations such as eIDAS make them acceptable and credible in various jurisdictions worldwide.
In fact, the EU actually encourages member states to adopt electronic signatures to simplify legal procedures and increase security.
Summary
Advanced Electronic Signatures (AES or AdES) offer you a secure and reliable way to sign electronic documents, using methods like ID verification. They are secure, unique, identifiable, and trackable. So, if you want to sign any legal document or agreement with a medium to high level of importance, AES is a good option.
Want to try signing a document using Advanced Electronic Signature?
Sign
any
Document in Less than
a Minute.

Frequently Asked Questions
- Do advanced electronic signatures work across different countries and legal jurisdictions?
- Yes, advanced electronic signatures are designed to be internationally recognized, but the acceptance and legal validity may vary between countries due to differing regulatory frameworks. Some countries may require specific standards or mutual recognition agreements for cross-border validity.
- Are there specific industries or use cases where advanced electronic signatures are mandated or preferred?
- Advanced electronic signatures are often mandated or preferred in industries with stringent regulatory requirements, such as healthcare (HIPAA compliance), finance (SEC regulations), and government (eIDAS regulation in the EU). They are also favored for high-value transactions and contracts.
- How do advanced electronic signatures protect against fraud and tampering?
- Advanced electronic signatures employ cryptographic techniques to bind the signature to the document and the signer's identity. This includes using secure algorithms and hashing methods to detect any changes to the document after it has been signed, thereby safeguarding against fraud and tampering.






