Electronic Signatures: Complete Guide
11 min read
Electronic signatures (eSignatures) are a secure and efficient way to sign electronic documents. They are widely accepted throughout the world and, therefore, legally binding. But what exactly is considered an eSignature, and are they safe to use? In this guide, we’re going to answer all questions about eSignatures, from the formats and usage to legality concerns. This way, you can sign your documents electronically with confidence. So, let’s dive in!
Table of contents
- What is an Electronic Signature?
- What Are the Types of Electronic Signatures?
- What’s the Difference between an Electronic Signature and a Digital Signature?
- What Are the Acceptable Forms of Electronic Signatures?
- How to Create and Use an Electronic Signature?
- How Electronic Signatures Work in fynk?
- What Are the Benefits of eSignatures?
- Are Electronic Signatures Legally Binding?
- Which Documents Can You Sign Using eSignatures?
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions
Guides on How to Sign...
What is an Electronic Signature?
An electronic signature (eSignature) is a quick, safe, and efficient method to sign electronic documents using a digital device like a laptop, tablet, or smartphone. eSignatures are legally binding and, in some cases, can replace the signer’s handwritten signature.
They are commonly used to sign contracts, rental agreements, permission slips, offer letters, and any document that is in digital form, such as a PDF or Word file.
What Are the Types of Electronic Signatures?
Depending on the use case and the importance of the digital document being signed, there are different types of electronic signatures with different levels of security.
These eSignature types are defined by the regulations around the world. For example, eIDAS in Europe and the Federal ESIGN Act in the US are the regulations that define different types of electronic signatures, including:


1. Simple Electronic Signatures (SES)
Simple Electronic Signatures (SES) are the most basic type of eSignatures. The main use of this type of eSignature is for declaring the signer’s “confirmation” or “contest.” SES has no strict requirements like ID verification or signature validation. That’s why you can use SES for every day, low-risk digital signings such as receiving a postal package or clicking on the “I agree” button when visiting a website.
2. Advanced Electronic Signatures (AES)
Advanced Electronic Signatures (AES or AdES) are trackable eSignatures that are unique and linked to the signer via encrypted codes. When using AES, signers go through a simple ID verification, such as two-factor authentication (2FA), which is used to create a unique digital certificate that validates the signature.
Since Advanced Electronic Signatures are the sweet spot between security and convenience, they are the most common type of eSignature.
You can use AES when electronically signing medium to high-risk transactions and agreements, such as submitting tax returns or signing an NDA.
3. Qualified Electronic Signatures (QES)
Qualified Electronic Signatures (QES) are the most secure type of eSignature and are equivalent to handwritten signatures. QES is a type of Advanced Electronic Signatures with two extra levels of security:
a) Signers must obtain a Qualified Digital Certificate, which is issued by a Qualified Trust Services Provider (QTSP). To get this certificate, signers have to go through high-level ID verifications.
b) Signers have to use a Qualified Electronic Signature Creation Device (QSCD) when electronically signing the documents. This device can be hardware or cloud-based software that has integration with QES providers.
You can use QES when eSigning highly confidential or highly important contracts that involve a considerable amount of money or a lengthy valid period, like real estate or intellectual property agreements.
What’s the Difference between SES, AES, and QES?


Here’s a breakdown of differences between Simple Electronic Signatures (SES), Advanced Electronic Signatures (AES), and Qualified Electronic Signatures (QES):
| Feature | SES (Simple Electronic Signature) | AES (Advanced Electronic Signature) | QES (Qualified Electronic Signature) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Legal Recognition | 📜 Basic legal recognition in many jurisdictions. | 🛡️ Widely recognized, often accepted in legal proceedings and contracts. | 🏛️ Highest level of legal validity, mandated by regulations in some jurisdictions. |
| Authentication | 🖋️ Basic authentication of signer, typically username/password. | 🔍 More robust authentication methods like biometrics or two-factor authentication. | 📷 Rigorous authentication often involving face-to-face identification. |
| Security Measures | 🔒 Minimal security features, often lack encryption and audit trails. | 📈 Additional security measures like encryption, timestamping, and audit trails. | 🚀 Rigorous security standards including certificate-based authentication. |
| Integrity Assurance | 👀 Limited assurance of document integrity. | 🔐 Provides some level of assurance regarding document integrity. | 🔏 Ensures document integrity through cryptographic measures. |
| Non-Repudiation | 🚫 Limited non-repudiation capabilities. | 🛡️ Offers stronger non-repudiation, making it harder for signers to deny actions. | 🚫 Provides the strongest level of non-repudiation, minimizing disputes. |
| Regulatory Compliance | 📝 May not meet specific regulatory requirements. | ✅ Meets most regulatory requirements for electronic signing. | 📚 Fully compliant with legal standards and regulations. |
| Use Cases | 📧 Suitable for less sensitive documents or transactions. | 📊 Suitable for most business transactions and legal documents. | 💼 Ideal for highly sensitive or regulated transactions like contracts or financial agreements. |
💡 Good to Know: Both Advanced Electronic Signature (AES) and Qualified Electronic Signature (QES) require a special digital certificate to uniquely link the signer to the signature. However, the difference is that AES can use normal standard certificates, but in the case of QES, it must be a qualified certificate.
What’s the Difference between an Electronic Signature and a Digital Signature?
A digital signature is the underlying technology that makes electronic signatures secure by using a series of encrypted codes and mathematical schemes. So, all digital signatures are electronic, but not all electronic signatures are considered digital signatures.
In other words, when a digital signature is implemented in an electronic signature, it makes it an AES or QES.
A digital signature itself doesn’t look like a regular handwritten signature, but an electronic signature can. Based on Public Key Infrastructure (PKI), digital signatures are encrypted codes hidden within the document.
When a digital signature is implemented in an electronic signature, the document has extra qualities like:
- Authenticity: it guarantees the signer is the person that he/she claims to be.
- Non-repudiation: prevents the signer from denying they signed the document.
- Timestamp: a record showing the exact date and time of signing.
So, digital signatures are the factor determining whether electronically signed documents are secure, valid, and unique allowing for non-repudiation. These are the reasons why qualified electronic signatures are considered equivalent to handwritten signatures.
💡 Good to know: In general usage, “online signature” and “electronic signature” are often used interchangeably to refer to the same concept. Both terms describe the digital representation of a handwritten signature used to sign documents electronically.
What Are the Acceptable Forms of Electronic Signatures?
Electronic signatures can take on one of the following forms (in terms of appearance):
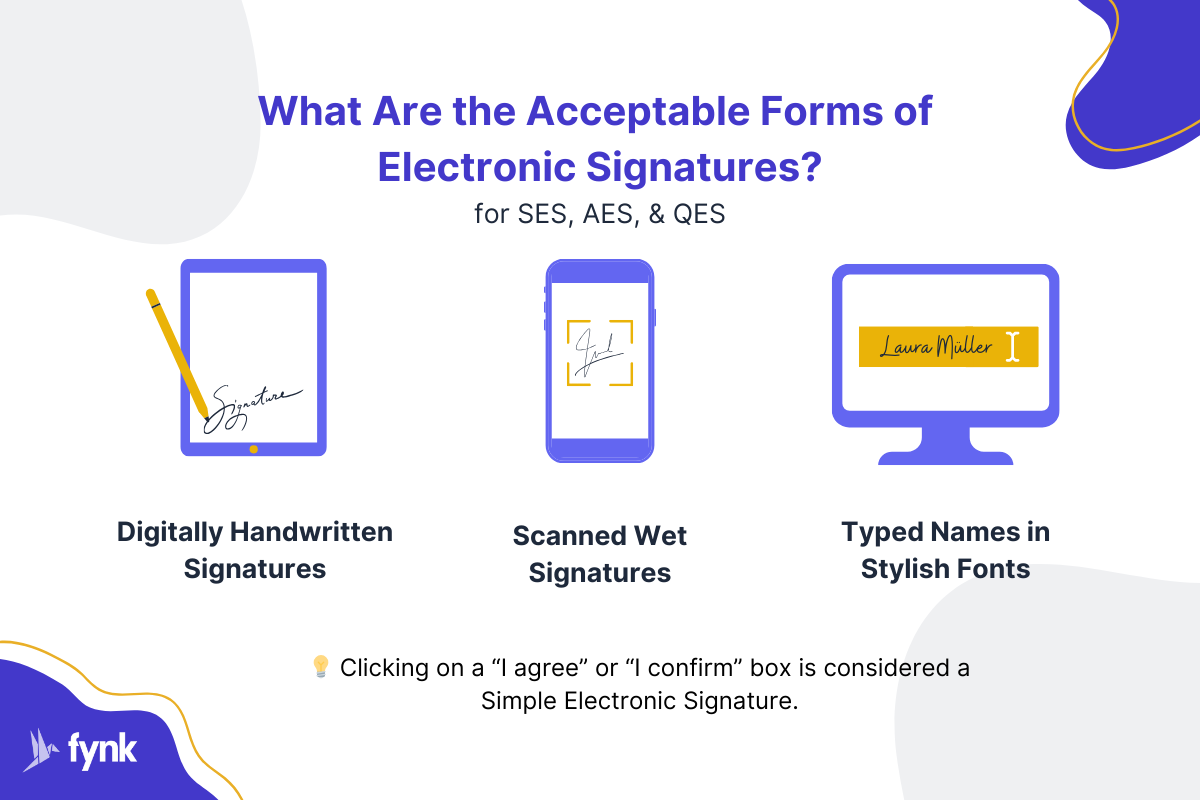

- Electronic drawing of your signature using a mouse, touchpad, or a digital pen
- Typed names, usually in stylish fonts
- A scan or image of your wet signature
🧠 Did you Know? Clicking or checking an “I agree” or “I confirm” box is considered a Simple Electronic Signature.
How to Create and Use an Electronic Signature?
You can use a trusted and secure eSignature platform such as fynk to easily create any forms and types of electronic signatures and electronically sign your documents.
All you have to do is upload your documents into the platform and use one of the signature forms mentioned above to create your eSignature.

In the case of Advanced and Qualified Signatures, you need to also complete the authentication process.
On your eSignature platform, invite other parties and signatories via email, and track the process of signing in real-time.
📌 Important: In the case of using AES and QES, make sure you use an eSigning platform that has eIDAS and GDPR compliance so that the eSignatures you create/request are legally binding.
If you only want to create and use a Simple Electronic Signature (SES)
You may use an in-build feature in text processing programs like Microsoft or Word and draw your signature or upload its file to the document.
How Electronic Signatures Work in fynk?
fynk is a secure and user-friendly eSigning and digital contract management platform that offers all three types of eSignatures.
fynk makes it easy for you to sign any contract and other legal documents. It’s made in Europe and complies with eIDAS regulations and GDPR to offer you legally binding signatures and the safest, yet easiest eSigning experience.
Using the platform, you can create the documents from scratch or simply use the contract templates available, so that you won’t have to go through the process of contract creation.
It also has features like real-time commenting, tracking, audit trail, and alerts that facilitate the contract negotiation phase and speed up the signing process.
Sign up for fynk now to try all the premium features for free!
Sign
any
Document in Less than
a Minute.

What Are the Benefits of eSignatures?
Electronic signatures are not just efficient and easy to use; they offer many other advantages for businesses, including:
Save You Tons of Money
Using electronic signatures can significantly cut your operating costs. Companies that use eSignatures reported an 80% decrease in document handling expenses.
Using eSignatures, you don’t need to pay for papers, envelopes, shipping, and postage. Not to mention that they don’t need a physical repository, so, there are no operating costs when you go digital.
They are also protected in safe cloud-based repositories, so you do neither have to be worried nor pay any fee to ensure the security of your files.
Offer the Highest Level of Security
Electronic signatures are much more secure than wet (handwritten) signatures for several reasons.
There’s always the possibility to fake a wet signature, but electronic signatures, especially the qualified ones, are almost impossible to forge.
Electronic signatures can be heavily encrypted to secure both the document content and the signature itself during transmission and storage. Once you initiate the eSigning process, none of the parties involved can make any changes to the document.
Skyrocket The Conversion Rate
If you switch to electronic signatures, your business could enjoy up to a 400% increase in conversion rate due to faster deal closures.
With electronic signatures, there’s no need for paper or waiting for in-person signatures. Your customers can sign contracts quickly from anywhere, which speeds up the sale cycle.
With a whopping 60% adoption rate, sales teams however aren’t the only ones benefiting from this trend. Marketing and finance teams with an average employment rate of 55% are also increasingly integrating digital documentation tools into their workflows
Higher Customer Satisfaction
Because they make the signing process so easy and fast, electronic signatures can boost the customers’ loyalty by 500%.
Even in the case of qualified electronic signatures which require higher levels of ID verification, eSignatures are still more convenient than traditional ones.
Customers experience smoother and faster service, leading to greater satisfaction and an overall improved experience with your business.
Are Electronic Signatures Legally Binding?
Yes, all three types of electronic signatures, including simple, advanced, and qualified, are legally binding.
Electronic signatures are widely accepted worldwide, with most countries having specific regulations that govern them. However, in most cases, these regulations complement each other smoothly.
The legal validity of electronic signatures may vary slightly from one country to another. Under the EU eIDAS regulation for example, just because a signature is electronic, it does not mean it cannot be legally effective. Even in some cases, a simple electronic signature (with low security) can be accepted.
Which Documents Can You Sign Using eSignatures?
Here are some of the cases that you can sign a document electronically:
- Legal Documents: Employment contracts, Non-Disclosure Agreements (NDAs), Sales Contracts, Service Agreements, Partnership Agreements
- Court Filings: Pleadings, Motions, and Briefs (where permitted by court rules)
- Business Documents: Purchase Orders, Invoices and Billing, Vendor Agreements, Sales Agreements, Board Resolutions, Internal Approvals
- Human Resources Documents: Employment Agreements, Onboarding Documents, Performance Reviews, Leave Requests, Policy Acknowledgements
- Financial Documents: Loan Agreements, Account Openings, Insurance Policies, Investment Agreements
- Real Estate Documents: Purchase Agreements, Lease Agreements, Property Management Forms, Mortgage Documents
- Government and Public Sector Documents: Permit Applications, License Renewals, Regulatory Filings
- Healthcare Documents: Patient Consent Forms, Medical Records, Insurance Claims
- Educational Documents: Enrollment Forms, Student Records, Parental Consent Forms
- Other Documents: Non-Profit Agreements, Event Registrations, Surveys and Polls
💡 Good to know: In some rare cases, an electronic signature might not be acceptable. For instance, according to US law, if the parties involved do not intend to form a contract electronically, the validity of a signature provided in this manner may be questioned.
Conclusion
With most countries taking steps toward digitalization, electronic signatures are becoming more and more the norm. That’s why it’s important to learn how to create and use them securely.
Learning about the different methods and their appropriate applications helps you to choose the right level of security for your needs.
Ready to get started? Try fynk, the user-friendly eSignature platform that simplifies the process for you and your clients.
Sign
any
Document in Less than
a Minute.
Frequently Asked Questions
- 1. Is It Possible to Forge Electronic Signatures?
- Yes, like traditional signatures, electronic signatures can be forged. However, reputable electronic signature solutions like fynk use advanced security measures such as encryption, authentication, and audit trails to minimize the risk of forgery.
- 2. How Do You Verify an Electronic Signature?
- Verification methods depend on the type of electronic signature. Some rely on verification codes sent to the signer's phone (AES), while others use qualified certificates that can be validated by trusted providers (QES).
- 3. Do Electronic Signatures Require Certification?
- There are different levels of electronic signatures. Simple signatures, like typing your name, might not require certification. However, advanced electronic signatures, including qualified electronic signatures, which offer stronger security, often use digital certificates issued by trusted authorities.
- 4. Do Electronic Signatures Need a Witness for Validity?
- In most cases, electronic signatures don't require a physical witness. However, specific regulations or requirements for certain documents might dictate otherwise.
- 5. Can You Type Your Name to Create an Electronic Signature?
- Yes, typing your name in a designated signature field can be a basic form of an electronic signature. While it's legally recognized in many cases, it offers less security compared to other methods.
- 6. Is It Possible to Generate Electronic Signatures at Scale?
- Yes, eSignature platforms like fynk are designed to handle mass signing needs efficiently. These platforms allow multiple parties to sign documents electronically in a secure and streamlined way.
- 7. Are Electronic Signatures Admissible in Court Proceedings?
- Yes, electronic signatures are generally admissible in court as long as they meet specific legal requirements for validity within your jurisdiction. The level of security used in the electronic signature may also be a factor in how it's treated in court.
- 8. What Is eIDAS?
- eIDAS stands for 'Electronic Identification, Authentication and Trust Services.' It is a regulation established by the European Union (EU) that sets forth standards for electronic signatures, electronic identities, electronic seals, and other trust services within the European Single Market. eIDAS aims to facilitate secure electronic transactions and increase trust in electronic communications and online services across EU member states. It provides a legal framework for the recognition and acceptance of electronic signatures and other electronic trust services, ensuring their validity and legal effect across borders within the EU.
- 9. What's the difference between electronic signatures and electronic seals?
- Electronic signatures indicate an individual's intent to agree to a document, while electronic seals authenticate the origin and integrity of a document or message. Signatures are typically associated with individuals, while seals are often linked to organizations or entities. Both play crucial roles in digital authentication and trust.












