Purchase Order (PO) Template for Products
Purchase order templates streamline procurement by providing a consistent format for specifying product requirements, pricing, delivery and payment terms.
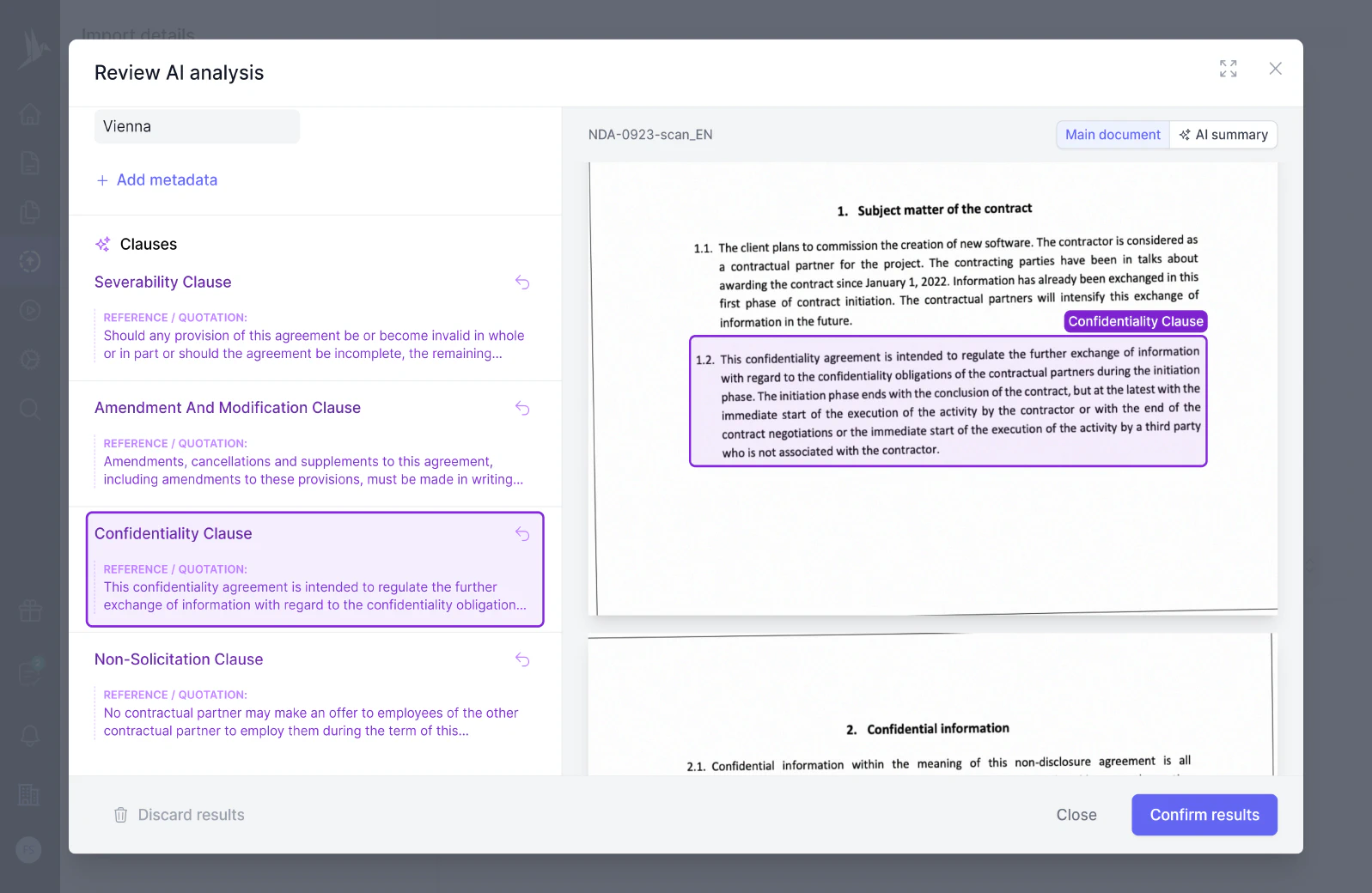
The "Remedies for Breach" clause outlines the legal consequences and available actions if one party fails to fulfill their obligations under the contract. It typically specifies the types of remedies, such as damages, specific performance, or termination, that the non-breaching party may pursue to address the breach and mitigate its impacts.
Remedies for Breach of Obligations under the Covenants Not to Solicit Above. The following is added to the end of the paragraph entitled “Remedies for Breach of Obligations under the Covenants Not to Solicit Above” of the Employment Agreement: “You agree and acknowledge that BHC shall at all times following the date hereof have the right to enforce, and be an express third-party beneficiary hereunder with respect to, your obligations under the Covenant Not to Solicit of this Agreement and, accordingly, that BHC shall have all of the rights and remedies (including to the right to obtain injunctive relief against any breach or prospective breach of such obligations by you) as are afforded under this Agreement to the Company.”
Remedies for Breach. Executive acknowledges that the legal remedies for breach of the covenants contained in Sections 6 and 7 may be inadequate, and therefore agrees that, in addition to any or all other remedies available to Company in the event of a proven breach of any covenant contained in Sections 6 or 7, Company may seek to obtain preliminary and permanent injunctions against any and all such actions without posting any bond.
Remedies For Breach. SCA and Company mutually agree that any breach of this Agreement by SCA or the Company may cause irreparable damage to the other party and/or their affiliates, and that monetary damages alone would not be adequate and, in the event of such breach or threat of breach, the damaged party shall have, in addition to any and all remedies at law and without the posting of a bond or other security, the right to an injunction, specific performance or other equitable relief necessary to prevent or redress the violation of either party's obligations under such Sections.
Remedies. Without in any maimer whatsoever limiting other possible remedies for breach of the covenants contained in this Article 5 , notwithstanding anything to the contrary elsewhere contained or other remedies available to the Employer, the Employee agrees that injunctive or other equitable relief shall be available to enforce such covenants, such relief to be without the necessity of posting a bond, cash or otherwise.
Remedies for Breach. In the event that Consultant willfully and materially breaches Consultant’s obligations under this Agreement, in addition to whatever other rights the Company may have, Consultant shall forfeit his right to receive any further payments or benefits under this Agreement.
Remedies for breach of the terms of the Local Addendum. If you breach the terms of the Local Addendum or otherwise breach any of the agreements or covenants set forth in this Notice of Grant you agree that in addition to any other provisions that are enforceable against you or remedies available to Price Group under the terms of the 2020 Long-Term Incentive Plan Price Group, all unvested Stock Units then held by you will be immediately forfeited for no consideration.
Remedies for Breach of Sections 6, 7, 8 and 9. Executive and Company agree that the covenants in Sections 6, 7, 8 and 9 are reasonable covenants under the circumstances. Executive agrees that any breach of the covenants set forth in Sections 6, 7, 8 and 9 of this Agreement will irreparably harm the Company. The Executive and the Company agree that in the event of any breach by the Executive of the provisions set forth in Sections 6, 7, 8 and 9 of this Agreement, the Company shall be entitled to all rights and remedies available at law or in equity, including without limitation, the following cumulative and not alternative rights: (1)the right to obtain injunctive or other equitable relief to restrain any breach or threatened breach or otherwise to specifically enforce the provisions of this Agreement, it being agreed that monetary damages alone would be inadequate to compensate the Company, the amount of such damages will be difficult (if not impossible) to prove precisely, and would be an inadequate remedy for such breach; (2)the right to institute civil suit to recover damages suffered by the Company; (3)the right to recover actual reasonable attorneys’ fees and other costs incurred by the Company in connection with pursuing remedies hereunder; and (4)the right to seek an equitable accounting of all earnings, profits and other benefits arising from any such violation.
Remedies for Breach. Participant stipulates that the covenants contained herein are essential for the protection of the trade secrets, confidential business and technological information, relationships, and competitive position of the Company; that a breach of any covenant contained herein would cause the Company irreparable damage for which damages at law would not be an adequate remedy; and that, in addition to damages and other remedies to which the Company would otherwise be entitled, it will be entitled to whatever injunctive relief is appropriate for any such breach.
The Pledgee shall have the right to choose to exercise any or all remedies for breach of contract that it is entitled to simultaneously or successively. The Pledgee does not need to exercise other remedies for breach of contract prior to exercising its rights to auction or sell off the Equity hereunder.
Remedies for Breach 16. Employee acknowledges that the legal remedies for breach of the provisions of this Exhibit may be found inadequate and therefore agrees that, in addition to all of the remedies available to Company in the event of a breach or a threatened breach of any of such provisions, the Company may also, in addition to any other remedies which may be available under applicable law, obtain temporary, preliminary and permanent injunctions against any and all such actions.
Remedies for Breach of this Agreement. Participant acknowledges and agrees that a breach of the covenants, promises, agreements and obligations set forth in this Agreement will result in material and irreparable injury to Company for which there is no adequate remedy at law, and that it would not be possible to measure damages for such injury precisely. In the event of such a breach or threat thereof, the Company shall have the right to seek, in addition to money damages, a temporary restraining order, preliminary injunction or permanent injunction restraining Participant from engaging in the activities prohibited by this Agreement, or any other relief as may be appropriate in law or equity or required for specific enforcement of the covenants set forth in this Agreement.
A remedy for breach refers to the legal solutions available when one party fails to fulfill their obligations under a contract. When a breach occurs, the non-breaching party can seek remedies to either enforce the contract or seek compensation for losses. Remedies are typically outlined within the contract itself and can include damages, specific performance, rescission, or reformation.
You should use a remedy for breach when one party to a contract fails to adhere to the terms agreed upon, impacting the contractual relationship. Remedies are crucial to protect the non-breaching party’s interests and seek compensation or restoration. It is essential to assess the nature of the breach—whether it’s a minor breach (non-material) or a major breach (material)—to determine the appropriate remedy.
When writing a remedy for breach, precise and clear language should be used to articulate the remedies available should a breach occur. The clause should cover:
Example:
In the event of a breach, the non-breaching party shall provide written notice to the breaching party, specifying the nature of the breach. The breaching party shall have 30 days to cure the breach. If the breach is not cured within this period, the non-breaching party may pursue remedies including, but not limited to, seeking damages or terminating this agreement.
Contracts that typically contain remedies for breach include, but are not limited to:
Ensuring that contracts contain clear remedies for breach is essential for effective risk management and legal protection.
These templates contain the clause you just read about.

Purchase order templates streamline procurement by providing a consistent format for specifying product requirements, pricing, delivery and payment terms.

A Sale of Goods Contract is a legally binding agreement in which a seller agrees to transfer goods to a buyer in exchange for payment.
Dive deeper into the world of clauses and learn more about these other clauses that are used in real contracts.
The "Remedies" clause in a contract outlines the actions or compensation available to a party when the other party fails to fulfill their contractual obligations. It specifies the rights and procedures for seeking redress, such as damages, specific performance, or termination of the contract, aimed at addressing breaches and restoring the affected party's interests.
The "Removal of Personal Property" clause delineates the responsibilities and time frame within which tenants or parties must vacate and remove their belongings from a premises upon termination or expiration of a lease or agreement. Failure to comply may result in items being considered abandoned, potentially leading to their disposal or storage at the owner's expense.
A renewal option allows one or both parties the right to extend the term of the agreement for an additional period under specified conditions. This clause typically outlines the procedure and notice requirements for exercising the option, along with any changes in terms or pricing for the renewal period.
Try our AI contract analysis and extract important clauses and information from existing contracts.
< <
Fill out the form and we will get in touch with you to give you a personal, customized demo of fynk.
Greetings!
I'm Markus, co-founder of fynk. After you've submitted the form, I'll swiftly get in touch with you.
Also, right after you submit your details, you can pick a time that works best for you for our meeting.

