Operating Agreement Template for LLCs
A comprehensive operating agreement template defining LLC formation, management structure, member rights, and financial arrangements.
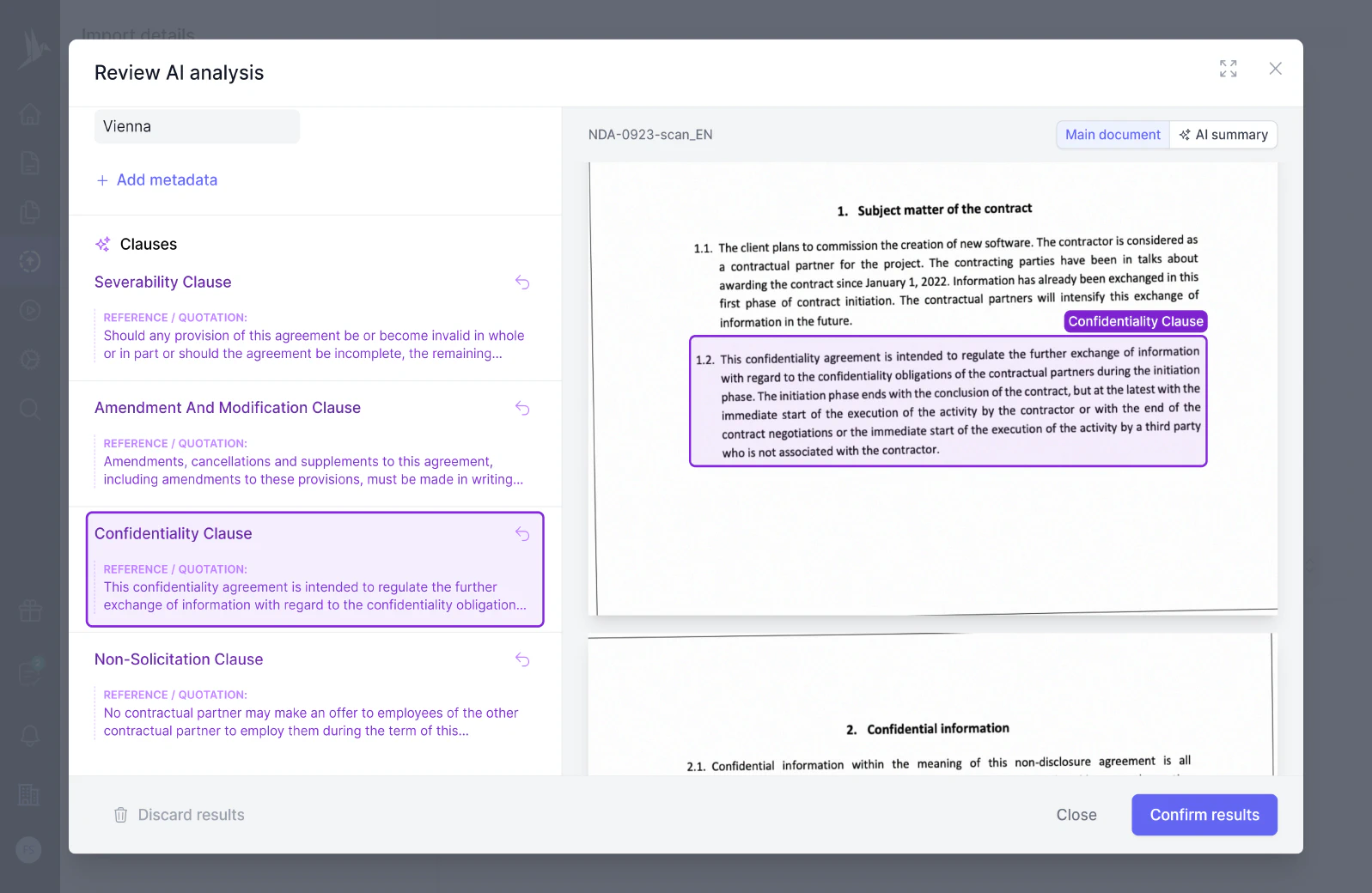
The "Right to Audit" clause grants a party the ability to review and examine the financial records, systems, and practices of another party to ensure compliance with contractual terms and accuracy of financial reporting. This clause is often included to provide transparency and accountability, and to safeguard against fraud or mismanagement.
Right to Audit. Kelly reserves the right to audit, inspect, and make copies or extracts of IC’s records and processes associated with IC’s performance under this Agreement at any time with twenty-four hours prior notice to IC. Any audit or inspection will occur during IC’s normal business hours. Kelly’s right to audit, inspect, and make copies or extracts of IC’s records and processes will continue for a period of five years following the termination or expiration of this Agreement unless IC certifies that IC has returned all related records to Kelly at the termination of this Agreement.
Nothing herein shall be deemed to grant to Frontier the right to audit internal records of Barclays regarding the revenues, income, or profits to Barclays of the Affinity Program, underwriting records, or generally.
Buyer shall have the right to audit Seller’s books and records to ensure compliance with the pricing as set forth in Attachment D pursuant to Section 20 of Attachment B.
Books and Records; Right to Audit. Hoth shall keep full, true and accurate books of accounts based on good accounting principles and other records containing relevant information and data which may be necessary to ascertain and verify the remuneration payable to Chelexa hereunder for a period of three (3) years following the year to which such records relate. During the Term and for a period of three (3) years following its termination, Chelexa shall have the right to audit, or have an agent, accountant or other representative, audit such books, records and supporting data upon thirty (30) days notice. Any audit shall be at Chelexa’s expense, except that Hoth shall reimburse Chelexa for the cost of the audit in the event that Chelexa discovers an underpayment often percent (10%) or more of the amount due.
The right to audit shall extend for three (3) years from delivery of any Net Unit Sales report. If a discrepancy is found, Cool Tech will pay any additional revenue percentage due within thirty (30) days, and in addition, if the discrepancy is greater than five percent (5%), Cool Tech shall reimburse Consortium for all reasonable audit costs incurred for the related audit.
Reserves the right to audit BIOFRONTERA premises and all documentation related to marketing and distribution of products in the US during normal business hours with reasonable written notice and causing minimum disruption to BIOFRONTERA operations.
Assignor shall have the right to audit and inspect no more frequently than once per year, the books and records of Assignee for purposes of the foregoing royalty interest. In the event that royalties paid are less than 90% of royalties due to Assignor, Assignee shall pay all expenses of such audit and inspection plus interest at a rate of six (6%) percent per annum.
The SBA reserves the right to audit any PPP loan.
The Agreement also contains other standard license terms including keeping of proper accounting records by Emerald and PetVivo having the right to audit such records, confidentiality requirements of both parties including adhering to the terms of a Prior Disclosure Agreement, customary indemnification and termination terms, responsibility of PetVivo to protect its Patent rights, procedures for the parties to address and prosecute any third party infringement of the Technology, standard warranties and representations by both parties regarding corporate structures and actions and ownership of Technology by PetVivo, lack of any pending or threatened material litigation, and resolution of any future disputes through a binding Alternative Dispute Resolution process.
Reinsurer will have the right to audit, remotely or at the Ceding Company’s office, the Ceding Company’s claims paying practices and procedures, including those practices and procedures applicable to claims eligible for the Program.
Upon reasonable request by a Party, the Parties shall permit one another or their representatives the right to audit the Information Security Programs and each Party’s data security policies and procedures, on reasonable advance notice during normal business hours, to confirm compliance with the requirements of this Agreement with respect thereto.
Mayfield shall have a right to audit TGV equivalent to TGV’s right to audit Mayfield under Section 4.6.
Licensor has the right to audit Licensee's accounting records upon three (3) days written notice.
Audit Rights: Tenant has the right to audit Landlord’s books and records relating to Operating Expenses for a period up to (i) three years following the receipt of any Statement for the Stabilized Adjustment Period and any Adjustment Period prior thereto, and (ii) two years following the receipt of any Statement for any Adjustment Period after the Stabilized Adjustment Period. Tenant has 180 days after Landlord makes such books and records available to complete the audit and 60 days thereafter to deliver the results to Landlord. If the results yield an overstatement of $50,000 or greater, Tenant will have the right to audit Landlord’s books and records for any Adjustment Period prior to the Adjustment Period which was the subject of Tenant’s audit.
COMPANY shall include in any sublicense granted pursuant to this Agreement, a provision that grants LICENSOR the right to audit the Sublicensee to the same extent that LICENSOR has the right to audit the COMPANY pursuant to Section 4.4 of this Agreement.
The Company maintains a right to audit Mr. Mann’s and/or Buyer’s records for up to one year following the final payment for all such engagements.
The “Right to audit” is a contractual provision that grants a party the ability to review and verify the accuracy and compliance of the other party’s records or operations. This right is often used to ensure that all terms, conditions, and obligations outlined in a contract are being followed. The audits can cover financial records, operational procedures, or compliance with specific terms.
You should consider using the right to audit in situations where transparency and accountability are crucial for maintaining trust in a business relationship. This includes contracts where financial transactions, data security, regulatory compliance, or performance metrics are involved. Key scenarios include:
When drafting a right to audit clause, it’s important to be specific about the scope, frequency, and procedure of the audits. Key elements might include:
Example Clause:
“The Client shall have the right to audit the records of the Service Provider pertinent to the delivery of services under this Agreement. Audits may be conducted upon thirty (30) days written notice and shall not occur more than twice per calendar year. The cost of such audits shall be borne by the Client, and all findings shall remain confidential and used solely for the purpose of verifying compliance with the Agreement.”
The right to audit is commonly included in several types of contracts where verification is necessary to uphold agreement terms. Typical contracts that contain right to audit clauses include:
By including a right to audit clause, parties can safeguard their interests by maintaining oversight over the contractual relationship.
These templates contain the clause you just read about.

A comprehensive operating agreement template defining LLC formation, management structure, member rights, and financial arrangements.
Dive deeper into the world of clauses and learn more about these other clauses that are used in real contracts.
The "Right to Encumber" clause allows a party to use property as collateral to secure a debt or obligation, potentially impacting the property's marketability or the rights of other stakeholders. It grants the holder the ability to place liens or mortgages on the asset, often subject to terms and conditions outlined in the agreement.
The "Right to Indemnification" clause in a contract ensures that one party (typically the indemnitee) is protected from any losses, damages, or liabilities incurred as a result of the actions or omissions of another party (the indemnitor). This clause obligates the indemnitor to compensate the indemnitee for any costs or legal fees arising from claims, effectively shifting the risk from one party to the other.
The "Right to Subcontract" clause allows a party in a contract to delegate their obligations or tasks to a third-party subcontractor, subject to any limitations or conditions outlined in the agreement. This clause typically ensures that the original party remains responsible for the performance of their contractual duties, even if those duties are executed by the subcontractor.
Try our AI contract analysis and extract important clauses and information from existing contracts.
< <
Fill out the form and we will get in touch with you to give you a personal, customized demo of fynk.
Greetings!
I'm Markus, co-founder of fynk. After you've submitted the form, I'll swiftly get in touch with you.
Also, right after you submit your details, you can pick a time that works best for you for our meeting.

