Articles of Association Template
The Articles of Association template sets the rules for how a company is run, including governance, shares, and voting.
A shareholding structure clause outlines the distribution of shares among the shareholders of a company, detailing each party's ownership percentage and the rights associated with their shares. This clause is crucial for defining voting power, profit distribution, and control within the company.
The shareholding structure of the Company after issue of the shares pursuant to the above paragraph is: 7,200,000,000 ordinary shares, of which 4,000,000,000 shares issued at the time of establishment of the Company, 870,000,000 domestic shares listed in the PRC and issued after the establishment of the Company, and 2,330,000,000 overseas listed foreign shares.
The share registration process of the first exercise of the share options under the initial grant of the A share share option incentive scheme was completed on 27 September 2017. The shareholding structure of the Company changed to: 10,814,176,600 ordinary shares, of which 7,319,176,600 domestic shares listed in the PRC, representing 67.68% and 3,495,000,000 overseas listed foreign shares, representing 32.32%.
KRY:the shareholding structure of KRY is as follows: (i) IPTH owns 873,834 shares, constituting 51% of the total shares in KRY; (ii) PG owns 839,565 shares, constituting 48.9994% of the total shares in KRY; and (iii) PropertyGuru International (Malaysia) Sdn. Bhd., a Malaysian subsidiary of PG, owns 1 share, constituting 0.0006% of the total shares in KRY.
Within three days after the signing of this agreement, Party A shall cause the Target Company to make a legal and valid shareholder meeting resolution and an amendment to the company’s articles of association (or to have the company’s articles of association amended), and Party A is obliged to arrange the Target Company, within 7 working days, to work on the procedures for the change of shareholding structure in the Shenzhen Municipal Administration for Market Regulation.
Both Party A and Party B shall prepare all the information for the change of shareholding structure required by Shenzhen Municipal Administration for Market Regulation, so as to ensure the smooth completion of the shares transfer.
The Parties agree to restructure the shareholding structure of Fujian Fulgent and to construct a VIE structure in accordance with the terms and conditions of this Agreement (the “Restructuring”).
EFFECTS ON THE SHAREHOLDING STRUCTURE OF THE COMPANY Immediately before the Conversion, the Company has 776,850,762 Ordinary Shares and 323,657,534 Preference Shares in issue and Yehuda Lisker holds 31,008 American Depository Shares (“ADSs”) of the Company representing 620,160 issued Ordinary Shares of the Company which representing approximately 0.08% of the total issued Ordinary Shares of the Company. Immediately after the Conversion and as at the date of this announcement, the Company has 777,446,915 Ordinary Shares and 323,657,534 Preference Shares in issue and Yehuda Lisker holds 31,008 ADSs and 596,153 Ordinary Shares representing a total of 1,216,313 issued Ordinary Shares of the Company which representing approximately 0.16% of the total issued Ordinary Shares of the Company. For illustrative purpose only, the shareholding structure of the Ordinary Shares and the Preference Shares (i) immediately before the Conversions and (ii) immediately after the issue of the 596,153 Conversion Shares is set out below:
The Parties hereto agree that in case of any change to Party C’s shareholding structure or any addition or deduction of any of Party C’s shareholders, Party A, Party C and Party C’s then-current shareholders shall re-sign this Agreement, and as of the effective date of the Equity Interest Pledge Agreement re-entered into by and among the foregoing parties, this Agreement will automatically terminate and become invalid.
The shareholding structure of GKZX was updated in both 2021 and 2022 and concurrent with each completion of equity transfer in GKZX, the previous contractual arrangements Beijing Rongsanliuling Information Technology Co., Ltd. entered into with GKZX and its then previous shareholders that provided Beijing Rongsanliuling Information Technology Co., Ltd. effective control over GKZX were terminated and a new set of contractual arrangements with the same terms were entered into with GKZX and its then current shareholders.
ArcelorMittal (the “Company”) announces that on 22 June 2020 it received two shareholding notifications from Société Générale SA. The notifications were made to reflect the entry into by Société Générale SA mainly of various financial instruments (as detailed in the notifications). According to the notifications, the following thresholds of voting rights were reached: - 5.99% on 16 June 2020, and - 4.66% on 17 June 2020. These notifications do not require any adjustments to the disclosure of the Company regarding its shareholding structure as the Company only reports shareholding thresholds above 5% on its website since, following the above-mentioned 17 June 2020 notification, Société Générale SA is again below this threshold. These notifications are available in the Luxembourg Stock Exchange’s OAM electronic database on www.bourse.lu and on the Company’s website corporate.arcelormittal.com under “Investors - Corporate Governance - Shareholding structure”.
As at the date of the Agreement, the shareholding structure of the Target Company is as follows Name of shareholders and Shareholding Structure: TIANO INTERNATIONAL HOLDINGS LIMITED 80.01% Powerbridge Holdings Limited 19.99%
A shareholding structure refers to the arrangement of the ownership of a company, detailing how its shares are distributed among its shareholders or stockholders. It outlines the proportion of stocks each shareholder holds, which consequently determines their influence and voting rights within the company. A clear shareholding structure provides insights into the power dynamics and decision-making processes within a company.
A shareholding structure is essential in several scenarios, including:
Writing a shareholding structure involves several specific steps:
Example:
Shareholder A: 1,000 shares - 40% ownership - 1 vote per share
Shareholder B: 500 shares - 20% ownership - 1 vote per share
Shareholder C: 1,500 shares - 60% ownership - 0.5 vote per share
Several contracts and legal documents often encompass a shareholding structure, including:
These templates contain the clause you just read about.

The Articles of Association template sets the rules for how a company is run, including governance, shares, and voting.
Dive deeper into the world of clauses and learn more about these other clauses that are used in real contracts.
A short form lease is a simplified version of a standard lease agreement that outlines the essential terms and conditions between the landlord and tenant, often omitting detailed provisions for the sake of brevity. This type of lease typically includes fundamental details such as the identification of the parties involved, property description, lease duration, rent amount, and basic obligations, while more complex terms may be addressed in supplemental documentation.
The Sick Leave clause outlines the conditions under which an employee can take time off due to illness, including the amount of leave allowed, any documentation required for extended absences, and whether the leave is paid or unpaid. It ensures that employees have the necessary time to recover from illness without fear of job loss or penalty.
A "sign-on bonus" clause refers to a financial incentive provided by an employer to a new employee as part of their employment agreement, typically paid upon the employee's commencement of work. This bonus is often used to attract top talent or compensate for potential losses incurred by the employee when leaving their previous job.
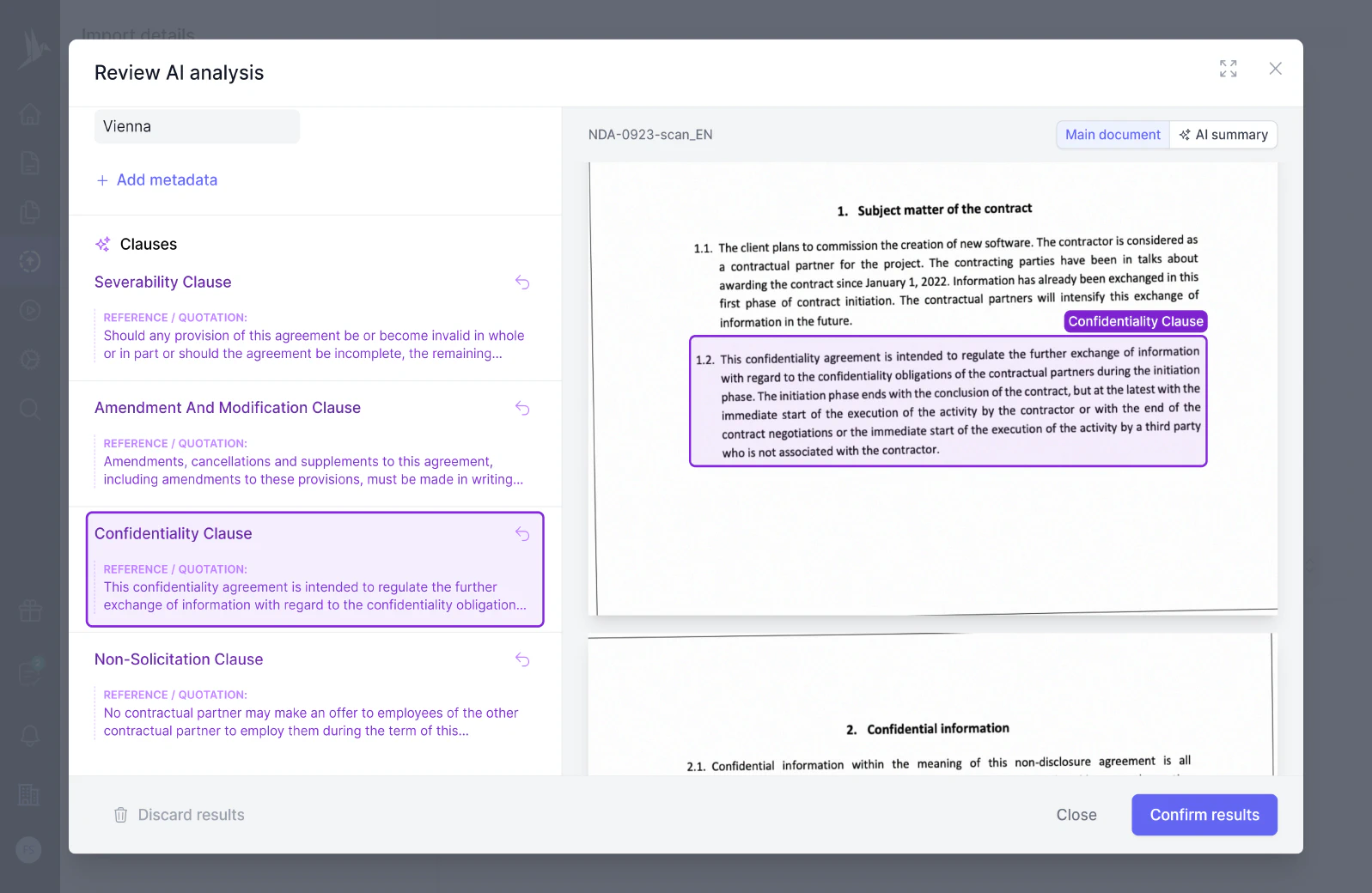
Try our AI contract analysis and extract important clauses and information from existing contracts.
< <
Fill out the form and we will get in touch with you to give you a personal, customized demo of fynk.
Greetings!
I'm Markus, co-founder of fynk. After you've submitted the form, I'll swiftly get in touch with you.
Also, right after you submit your details, you can pick a time that works best for you for our meeting.

