Cleaning Services Agreement Template for B2B
Define cleaning, maintenance, and payment terms between service providers and clients for professional cleaning contracts.
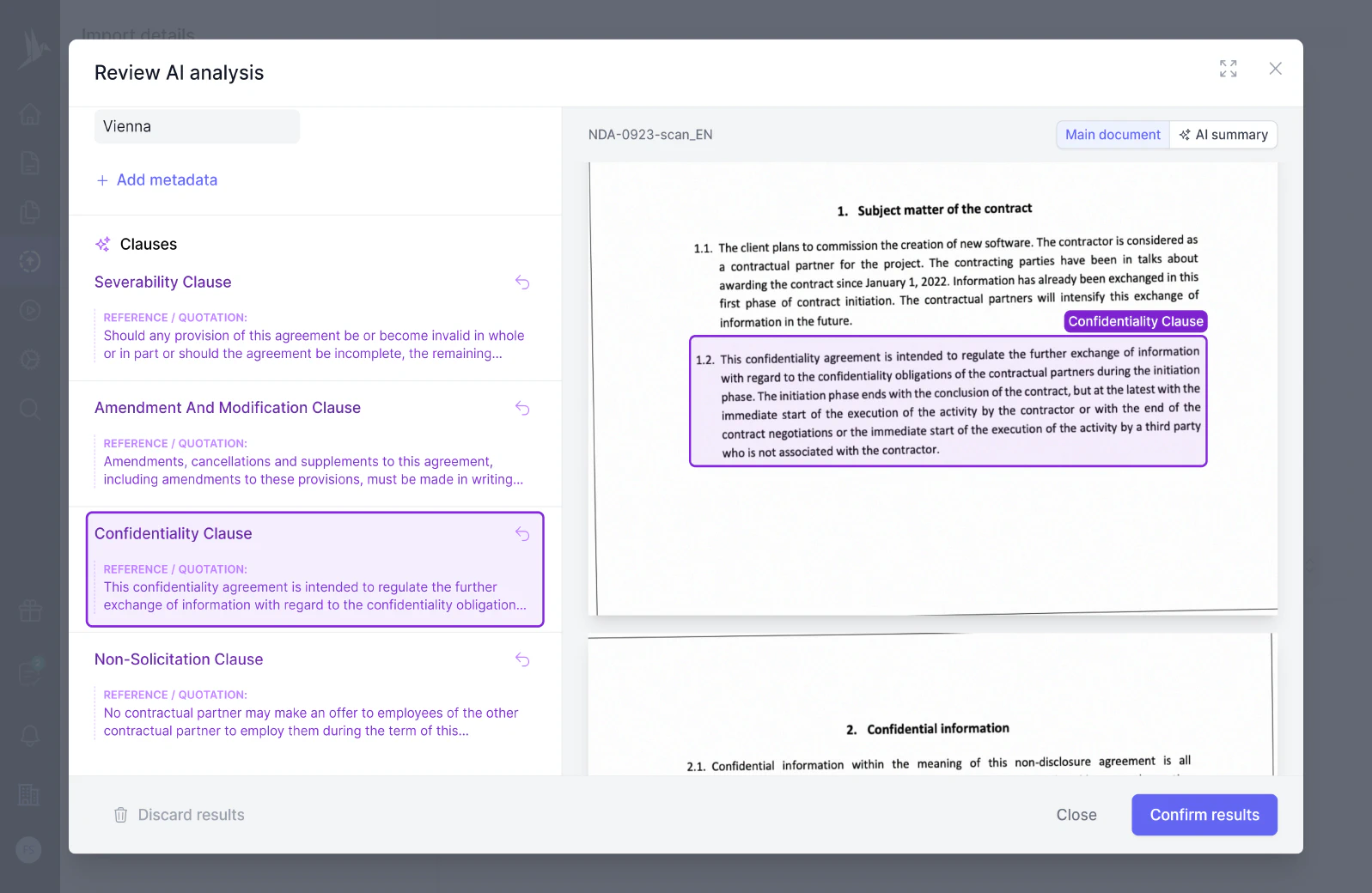
A "Liability for breach of contract" clause outlines the responsibilities and obligations a party faces if they fail to fulfill their contractual duties, including potential compensation for damages incurred by the non-breaching party. It typically specifies the extent and limitations of liability, such as caps on damages or exclusions of certain types of loss.
Liability for breach of contract if the Contractor fails to submit the labor contract and the proof of social insurance payment for the Project Manager: Ordered to submit the labor contract and make up the social insurance payment within a certain period of time.
Liability for breach of contract if the Project Manager leaves the construction site without approval: A penalty of 100 yuan for each day of absence.
Liability for breach of contract if the Contractor replaces the Project Manager without authorization: If the original Project Manager can continue to perform his/her duties, the Supervisor shall order the Contractor to cancel the replacement decision, and the Contractor shall bear liquidated damages of 10,000 yuan. If the original Project Manager is objectively unable to continue to perform his/her duties, the Client shall have the right to request an audit to confirm the Project Manager replaced by the Contractor, and the Contractor shall bear liquidated damages of 10,000 yuan.
Liability for breach of contract if the Contractor refuses to replace the Project Manager without good reasons: The Supervisor shall notify the Project Manager in writing to stop work on the 29th day after the Contractor is notified of the second replacement and shall direct that the construction be temporarily suspended. The suspension of construction caused by the Contractor shall be handled according to Article 7.8.2 of the General Conditions.
Liability for breach of contract if the Contractor refuses to replace the main construction management personnel without good reasons: The supervisor shall issue another notice requesting the Contractor to replace the main construction management personnel within 3 days and assume the liability for breach of contract in the amount of 5,000 yuan. If the Contractor still refuses to replace within 3 days after receiving the second notice, the Supervisor shall notify the main construction management personnel in writing to stop the work and instruct the temporary suspension of construction. The suspension of construction caused by the Contractor shall be handled according to Article 7.8.2 of the General Conditions.
Liability for breach of contract if the Contractor replaces the main construction management personnel without authorization: If the original management personnel can continue to perform his/her duties, the Supervisor shall order the Contractor to cancel the replacement decision, and the Contractor shall bear liquidated damages of 5,000 yuan. If the original management personnel is objectively unable to continue to perform his/her duties, the Client shall have the right to request an audit to confirm the management personnel replaced by the Contractor, and the Contractor shall bear liquidated damages of 10,000 yuan. The additional cost and delayed construction period as a result shall be borne by the Contractor.
Liability for breach of contract if the main management personnel of the Contractor leave the construction site without approval: A penalty of 500 yuan for each day of absence.
Delay due to the Contractor The calculation of liquidated damages for late completion due to the delay caused by the Contractor is as follows: Where the delay is caused by the Contractor (except force majeure) and the schedule cannot be postponed, the increase in cost of catch-up measures as a result shall be borne by the Contractor; meanwhile, the Contractor shall bear the liability for breach of contract and pay the Client liquidated damages of 500 yuan for each day the product duration is delayed. The Client may deduct such liquidated damages from any amount payable to the Contractor and the payment of such liquidated damages shall not relieve the Contractor of its obligation to complete the project and other obligations hereunder.
If Party B breaches Article 9 of this Agreement, Party B shall pay liquidated damages to Party A within 1 month from the date on which the liability for breach of contract is incurred, and the amount of which shall be calculated according to the following formula: Amount of Liquidated Damages = RMB200 per square meter * Area of the Plot (m2) * (1-Amount of Actually Achieved Sales Income/Agreed Amount of Sales Income).
If Party B fails to pay the tax amount payable as agreed in Article 11 hereunder when it is due (but the tax paid by Party B has reached 70% or more as agreed), Party B shall pay liquidated damages to Party A within 1 month from the date on which the liability for breach of contract is incurred, and the amount of which shall be calculated by the area of the Plot at the rate of RMB175 per square meter. If Party B fails to fulfill 70% or more of the annual tax payable as stipulated in Article 11 of this Agreement when it is due, it shall be deemed as a material breach by Party B, in such case, Party B shall pay liquidated damages to Party A within 1 month from the date on which the liability for breach of contract is incurred, and the amount of which shall be calculated by the area of the Plot at the rate of RMB475 per square meter.
In case of violation of the provisions of this contract, the defaulting party shall bear the liability for breach of contract in accordance with the relevant provisions of the Contract Law of the People’s Republic of China.
1. Where Party A violates the provisions of Article 4, 7, and 10 of this Contract, Party A shall bear the following liability for breach of contract: (1) Where Party A violates Article 4 of this contract, Party A shall bear the liability for breach of contract. Party B has the right to terminate this contract, and Party A shall pay Party B 50% (three million yuan) of the total transfer fee as a penalty. (2) Where Party A violates Article 7 of this contract, Party A shall bear the liability for breach of contract, and Party B has the right to demand compensation from Party A. (3) Where Party A violates Article 10 of this contract, Party A shall bear the liability for breach of contract, and Party B has the right to demand compensation from Party A. 2. Where Party B violates the provisions of Articles 6 and 8 of this Contract, Party B shall bear the following liability for breach of contract: (1) Where Party B violates the provisions of Article 6 of this contract, Party B shall bear the liability for breach of contract. Party A has the right to terminate this contract, and Party A has the right to demand compensation for losses from Party B. (2) Where Party B violates the provisions of Article 8 of this contract, Party B shall bear the liability for breach of contract, and Party A has the right to demand Party B to compensate for the losses.
Party B’s liability for breach of contract 1 if Party B has any of the following behaviors, Party A has the right to unilaterally terminate this contract and take back the booth. If Party A does not terminate this contract, it will not affect Party A’s right to require Party B to bear the liability for breach of contract: 1.1 those who are in arrears to pay promotion fees for more than 30 days (including 30 days). 1.2 Party B goes bankrupt or goes through liquidation procedures, except for the liquidation due to reorganization or merger. 1.3 due to Party B’s reason, the booth is sealed due to the enforcement of the people’s court. 1.4 other circumstances under which Party A is allowed to unilaterally terminate the contract in advance by laws, regulations or other terms of the contract. 2 Party A and Party B agree that if Party B has any of the following behaviors, Party A has the right to unilaterally terminate this contract. After the termination of this contract, Party A shall cancel the cooperation. If Party A does not terminate this contract, it will not affect Party A’s right to require Party B to bear the liability for breach of contract:
Party A’s liability for breach of contract 1 within the term of cooperation, Party B shall have the right to unilaterally terminate this contract in case of any of the following circumstances: 1.1 if Party A fails to deliver the booth within the time stipulated in this contract for more than 90 days. 1.2 Party A violates the agreement of this contract, which makes Party B unable to continue to use the booth according to the purpose agreed in the contract. 1.3 there is a major safety problem in the main structure of the booth provided by Party A, which has not been solved after repair, so that both parties cannot continue to use the booth as agreed in the contract. 1.4 Party A goes bankrupt or decides to dissolve, except for liquidation due to reorganization or merger. 1.5 due to Party A’s reason, the booth is sealed due to the enforcement of the people’s court. 1.6 the site is unable to operate normally for more than 30 consecutive days due to Party A’s operation and other reasons. 1.7 other circumstances under which Party B is allowed to unilaterally terminate the contract in accordance with the provisions of laws and regulations or other provisions of the contract.
Liability for breach of contract for overdue payment If Party B fails to pay the house payment as agreed in Article 3 hereof, it shall pay party A liquidated damages of 0.05% of the unpaid house payment every day. If party B fails to pay the house for more than 2 days, Party A shall have the right to terminate the contract. If Party A requests to terminate the contract, it shall return the house payment paid by Party B to Party B within 10 days from the date when the termination of the contract notice reaches Party B.
Liability for breach of contract for delay in handling the property right registration If the real estate ownership certificate cannot be obtained on schedule due to Party A or Party B, both parties agree to deal with the following ways: No-2_: 1. The breaching party shall pay the liquidated damages of 1 / yuan, and the contract shall continue to be performed. 2. If the contract is terminated and the transaction is terminated, the parties shall not hold each other liable for breach of contract. 3. Others: 0.05% of the total house payment is calculated by day from the overdue date.
Liability for Breach of contract If each party fails to perform the contract or fails to perform the contract as agreed, it shall bear the corresponding liability for breach of contract in accordance with relevant laws and regulations.
Liability for breach of contract if the transaction fails. 1. If Party A fails to sell the real estate to Party B as agreed herein, it shall pay party B a liquidated damages of 20% of the transaction price of the real estate and return all the expenses paid by Party B. 2. If Party B fails to buy the real estate as agreed herein, it shall pay party A a liquidated damages of 20% of the transaction price of the real estate.
Liability for breach of contract for delay of house delivery. If Party A fails to deliver the house within the time limit stipulated in this contract, it shall pay party B liquidated damages at 0.05% of the total house price every day. If party A fails to deliver the house within 2 days, Party B shall have the right to terminate the contract. If Party B requests to continue to perform the contract, the contract shall continue to perform, Party A shall pay party B liquidated damages according to the standard of 0. 05% of the total house price from the second date of the delivery date of the property to the actual date of delivery.
Liability for Breach of Contract 1. The shipper’s liability for breach of contract. 2. If the shipper does not pay the freight in accordance with Article 4.1, the shipper shall pay a late fee of 5‰ of the freight every day from the day after the payment due date. If the expiration date is more than 2 months, the carrier has the right to unilaterally terminate the contract, and the carrier reserves the right to recover the previous expenses.
Liability for breach of contract refers to the legal responsibility that a party incurs when they fail to fulfill their obligations as stipulated in a contract. This liability can result in the breaching party being required to compensate the non-breaching party for any losses or damages incurred due to the breach. The primary aim is to put the non-breaching party in the position they would have been in had the contract been performed as agreed.
You should consider issues of liability for breach of contract in situations where:
When writing a liability for breach of contract clause, consider the following elements:
Define the Breach: Clearly specify what constitutes a breach. Is it a failure to deliver goods, services, payment, or something else?
Measure of Damages: Outline how damages will be calculated or determined. This could include actual damages, consequential damages, or liquidated damages.
Limits of Liability: Specify any caps on damages, if applicable, and whether indirect or consequential damages are excluded.
Remedies and Resolution: Describe the remedies available to the non-breaching party and any dispute resolution mechanisms, such as mediation or arbitration.
Mitigation Requirement: State any obligation of the non-breaching party to mitigate their losses.
Example Clause: “In the event of a breach, the non-breaching party shall be entitled to recover all direct damages resulting from the breach, provided that such damages are not speculative, and that the non-breaching party has taken reasonable steps to mitigate such damages.
Liability for breach of contract clauses are typically found in:
Commercial Contracts: Such as supply agreements, service contracts, and sales contracts, where parties perform business transactions.
Employment Contracts: Detailing the responsibilities of employers and employees, and consequences of non-compliance.
Construction Contracts: Where performance timelines and quality standards are critical and breaches can lead to significant damages.
Lease Agreements: Outlining tenant and landlord obligations, and the penalties for failing to uphold them.
Licensing Agreements: Defining the scope and limitations on the use of intellectual property, with specific remedies for unauthorized use.
These clauses are a vital component of contract law that provides predictability and recourse in case of deviations from the agreed-upon terms.
These templates contain the clause you just read about.

Define cleaning, maintenance, and payment terms between service providers and clients for professional cleaning contracts.
Dive deeper into the world of clauses and learn more about these other clauses that are used in real contracts.
A "license back" clause grants the original owner of intellectual property some rights to use or exploit improvements made to that property by a licensee. This allows the licensor to benefit from enhancements or developments made by the licensee during the term of the license agreement.
A license fee clause outlines the payment terms and conditions under which a licensee is required to pay the licensor for the rights to use intellectual property, technology, or other licensed assets. It typically specifies the amount, frequency, and method of payment, and may also include adjustments based on usage, performance metrics, or renewals.
A license grant clause in a contract specifies the permissions and limitations under which the licensee can use the licensor's property, such as intellectual property or technology. It defines the scope, duration, territory, and conditions of the granted rights, thereby outlining the legal framework for usage and ensuring protection for the licensor's assets.
Try our AI contract analysis and extract important clauses and information from existing contracts.
< <
Fill out the form and we will get in touch with you to give you a personal, customized demo of fynk.
Greetings!
I'm Markus, co-founder of fynk. After you've submitted the form, I'll swiftly get in touch with you.
Also, right after you submit your details, you can pick a time that works best for you for our meeting.

